Affirmative,
negative and
interrogative forms
In this section, you will read, observe and study how to describe completed actions at specific times in the past. You will read about an unusual pet, and listen to the biography of a survivor from the “Titanic.” You will also write your autobiography and recycle time expressions. Next, you will remember a special celebration to write about it. Finally, you will learn and practice irregular verbs and the pronunciation of regular verbs in the past.
Look at the following pictures and think about these questions for a moment. Click on each image to see its description. Use the arrows to see the rest of the images.
By the end of this section, you will use the simple past tense in affirmative, negative and interrogative. You will make a distinction with WAS/WERE and recycle past time expressions, to ask and give information about people’s activities in the past.
In everyday life, we sometimes talk about events that happened in the past. Study and review the following presentation in order to identify some elements that we use to describe past events.
Click on the link to download the presentation.
These are the characteristics of the simple past tense contextualized in a day of a student like you. Now let’s check some verbs in past and their classification.
Do you remember some verbs in English? When we use them in the past tense, we classify them in regular and irregular verbs. Look at the following information.
| Add to most verbs- ED | Ask- asked Want- wanted Fail- failed Visit- visited |
| Verbs ending in –E add a - D | Bake- baked Dance- danced Like- liked Live- lived Hate- hated Love- loved |
| Verbs ending in CONSONANT + VOWEL + CONSONANT Double the last consonant and add - ED |
Stop- stopped Mop- mopped Skip- skipped Chop- chopped Shop- shopped |
| Verbs ending in CONSONANT + Y change “Y” to “I” and add - ED |
Study- studied Carry- carried Worry- worried Hurry- hurried Dry- dried |
Watch the video on this link Past Tense paying attention the rules to pronounce the regular verbs in the past.
Remember, Rule 1: If the verb base ends in a voiceless sound, then the –ed ending sounds like “t”. The “t” is blended together with the previous consonant and not pronounced as an extra syllable. Rule 2: If the verb base ends in a voiced sound, then the –ed ending sounds like “d”.
Now, do the following exercise to practice what you have studied about the pronunciation of regular verbs.
In the case of irregular verbs, you have to memorise their tense patterns or changes. Watch the following video on Youtube.
Click on the link irregular verbs to watch it.
Another tip to help you memorise them is to group them according to their patterns.
Group 1
All three forms of the verb are the same
| Base Form | Simple Past | Past Participle |
| bet | bet | bet |
| cost | cost | cost |
| cut | cut | cut |
| hit | hit | hit |
| hurt | hurt | hurt |
| let | let | let |
| put | put | put |
| shut | shut | shut |
Group 2
The 2nd and 3rd forms of the verb are the same
| Base Form | Simple Past | Past Participle |
| lose | lost | lost |
| shoot | shot | shot |
| get | got | got |
| light | lit | lit |
| sit | sat | sat |
| keep | kept | kept |
| sleep | slept | slept |
| feel | felt | felt |
| leave | left | left |
| meet | met | met |
| bring | brought | brought |
| buy | bought | bought |
| fight | fought | fought |
| think | thought | thought |
| catch | caught | caught |
| teach | taught | taught |
| sell | sold | sold |
| tell | told | told |
| pay | paid | paid |
| make | made | made |
| stand | stood | stood |
| understand | understood | understood |
| lend | lent | lent |
| send | sent | sent |
| spend | spent | spent |
| build | built | built |
| find | found | found |
| have | had | had |
| hear | heard | heard |
| hold | held | held |
| read | read (pronounced red) | read (pronounced red) |
| say | said | said |
Group 3
All three forms of the verb are different
| Base Form | Simple Past | Past Participle |
| drive | drove | driven |
| ride | rode | ridden |
| rise | rose | risen |
| write | wrote | written |
| bite | bit | bitten |
| hide | hid | hidden |
| break | broke | broken |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| wake | woke | woken |
| blow | blew | blown |
| grow | grew | grown |
| know | knew | known |
| draw | drew | drawn |
| fly | flew | flown |
| show | showed | shown |
| wear | wore | worn |
| tear | tore | torn |
| begin | began | begun |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| swim | swam | swum |
| ring | rang | rung |
| sing | sang | sung |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| forget | forgot | forgotten |
| give | gave | given |
| see | saw | seen |
| take | took | taken |
Now let’s practice. Can you make a distinction between a regular and irregular verb?
Do you remember Michelle’s conversation with Diana?
Click on each title to see the sentence structure in the simple past.
WAS/WERE IS NOT PART OF THIS TOPIC. Do not use it when you want to express actions in past.
Now, you will practice the structure of simple past in affirmative, interrogative and negative. In the first part, write the past form of the verb in the parentheses “()” to complete the sentences. In part two change affirmative sentences into negative sentences. Finally, in part three, change the negative sentences into interrogative sentences.
Keep in mind it is necessary to use the auxiliary DID in interrogative and negative ideas. In the case of affirmative ideas, you do not need an auxiliary; the verb goes in simple past.

Activity 1
The simple past tense is used to describe actions or events that take place in the past. Now you will have to do the following activity based on the contents of a text.
You will read a page of a teenager's diary about an unusual pet. Identify the events in the past and put them in order.

Activity 2
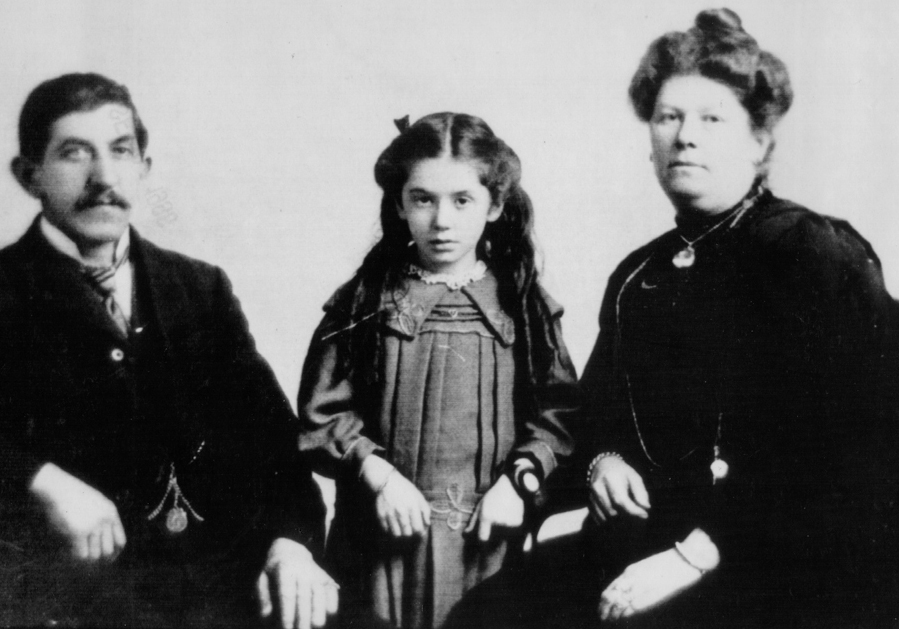

Eva/Esther Hart. (1910). Hart family [photo]. Retrieved on 2016, November 8 from http://bit.ly/2usFaxg |
You will identify specific information about past actions. Listen to a part of a recording from a survivor of the Titanic. Listen to the audio twice and pause if necessary. Based on the information, answer or complete the sentences.
|


Activity 3
|
In this activity, you will have to write your autobiography by answering the questions on the right. To have a better idea, look at the example provided. |
When were you born? How old are you? Where did you study elementary school? Did you meet good friends in there? What did you do during junior high school? How did you decide to study the major you are studying? When did you receive your first kiss? Did fall in love with someone special? Where and when? |
This is my autobiography.
My name is Stella. I was born in Quito, Ecuador. I am 23 years old and studied elementary public school in a town near Quito. It was a great small school. All the children in the town went there to study. There were not many students, and I had good friends there. When I was 15, I moved to Mexico City and studied in a public high school. It was difficult because I did not know many people, it was very crowded and noisy. It was difficult for me to adapt. I remember people in my group were loud, but now I know that is the Mexican style. They were great with me, and we went to many parties. Then I decided to study art. I remember painting since I was a little girl and everybody loved what I did.
When I was 15 I got my first kiss, it was a goodbye kiss because I was moving to Mexico. German, a boy who studied with me, didn’t want me to return to Ecuador. He was very friendly and kind to me. I liked him very much, but I did not love him. People from Ecuador are friendly and generous. We love our freedom, and in my case, I take love pretty seriously. That is why I think I have never fallen in love.
When you finish, use the rubrics to evaluate your progress.

Activity 4
|
Do you remember a special birthday celebration? Think of the answers to these questions. • When was it? You will record yourself describing that day. It is important that you use complete ideas in past tense and that you answer all the questions. Your description should be organized in three paragraphs. |
Read the example carefully so that you have an idea of what to record for your description. 
|
Now that you know the rules and use of past tense, complete the following exercise.
You will complete a text writing in the box the verbs in the parenthesis in past tense in affirmative, negative or interrogative. To evaluate your answer click on the Check button. At the end of the exercise, you will know your score.
• Murphy, R. (1997). Essential grammar in use: A self-study reference and practice book for elementary students of English: with answers. Cambridge, U.K: Cambridge University Press.
• Oxenden, C. Latham-Koenig, C. (2013). American English File 1. Oxford, U.K. Oxford University Press.
• Coe, N., Harrison, M. y Patrson, K. (2006). Oxford Practice Grammar. Oxford, U.K: Oxford University Press.
• Coordinación de Universidad Abierta y Educación a Distancia-UNAM. (2011). English Media. Retrieved on 2016, November 13 from http://www.cuaed.unam.mx/english_media/.
• Elemental English. (2013). [t], [d] or [ld]? | "-ed" Past Tense | English Pronunciation [video]. Retrieved on 2016, November 13 from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j32SurxnE4s
• Michael English. (2014). MC Fluency – Irregular verbs rap with lyrics [video]. Retrieved on 2016, November 13 from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3P5StOplPbM.